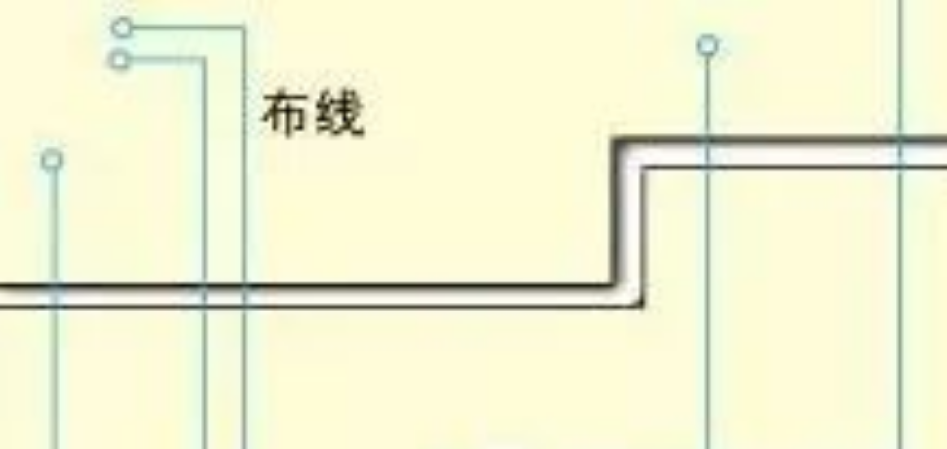
In the process of PCB design, the division of the power plane or the division of the ground plane will lead to the incomplete plane. In this way, when the signal is routed, its reference plane will span from one power plane to another power plane. This phenomenon is called signal span division.
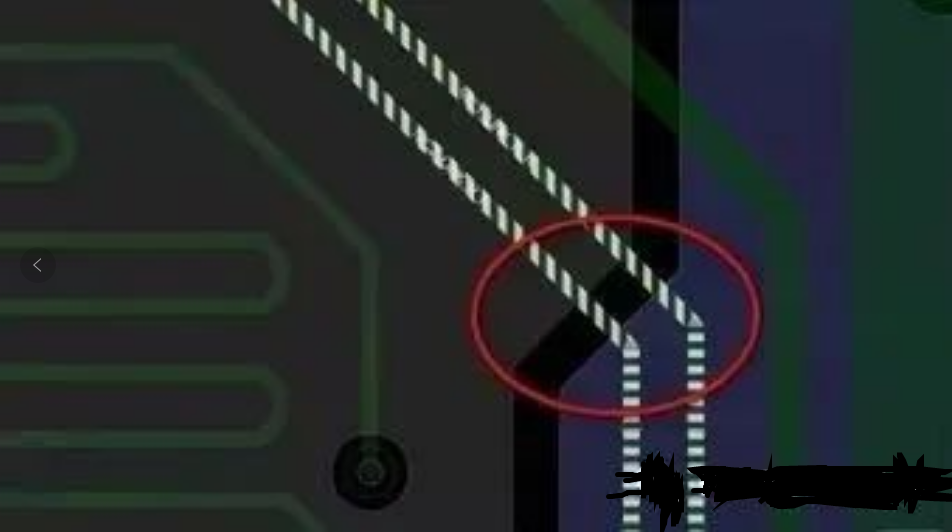

Schematic diagram of cross-segmentation phenomena
Cross segmentation, for the low speed signal may have no relationship, but in the high speed digital signal system, the high speed signal takes the reference plane as the return path, that is, the return path. When the reference plane is incomplete, the following adverse effects will occur: cross-segmentation may not be relevant for low-speed signals, but in high-speed digital signal systems, high-speed signals take the reference plane as the return path, that is, the return path. When the reference plane is incomplete, the following adverse effects will occur:
l Impedance discontinuity resulting in wire running;
l Easy to cause crosstalk between signals;
l It causes reflections between signals;
l The output waveform is easy to oscillate by increasing the loop area of the current and the inductance of the loop.
l The radiation interference to space is increased and the magnetic field in space is easily affected.
l Increase the possibility of magnetic coupling with other circuits on the board;
l The high frequency voltage drop on the loop inductor constitutes the common-mode radiation source, which is generated through the external cable.
Therefore, PCB wiring should be as close to a plane as possible, and avoid cross-division. If it is necessary to cross the division or cannot be near the power ground plane, these conditions are only allowed in the low speed signal line.
Processing across partitions in design
If cross-division is inevitable in PCB design, how to deal with it? In this case, the segmentation needs to be mended to provide a short return path for the signal. Common processing methods include adding the mending capacitor and crossing the wire bridge.
l Stiching Capacitor
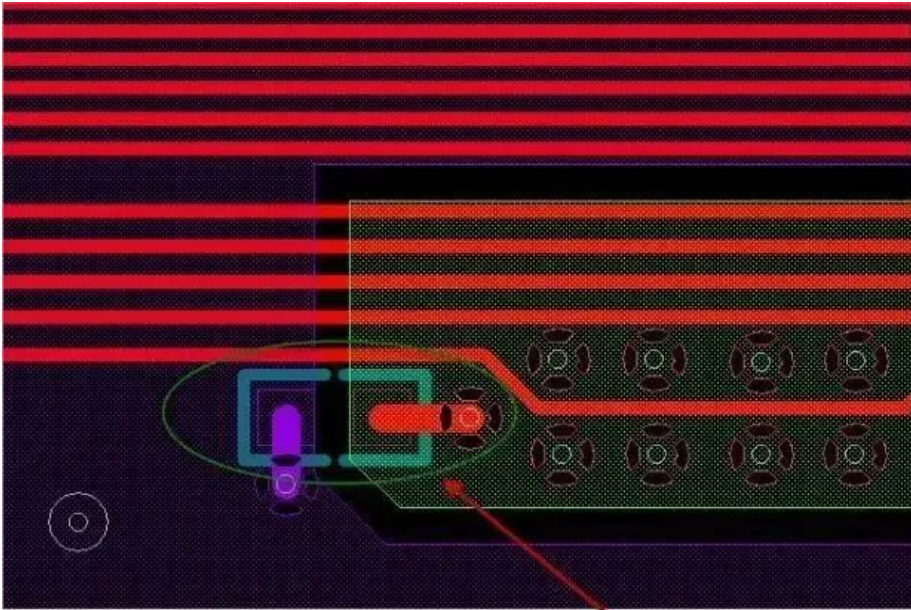
An 0402 or 0603 ceramic capacitor with a capacity of 0.01uF or 0.1uF is usually placed at the signal cross section. If space permits, several more such capacitors can be added.
At the same time, try to ensure that the signal wire is within the range of 200mil sewing capacitance, and the smaller the distance, the better; The networks at both ends of the capacitor respectively correspond to the networks of the reference plane through which the signals pass. See the networks connected at both ends of the capacitor in the figure below. The two different networks highlighted in two colors are:
l Bridge over wire
It is common to “ground process” the signal across the division in the signal layer, and may also be other network signal lines, the “ground” line as thick as possible
High speed signal wiring skills
a) multilayer interconnection
High speed signal routing circuit often has high integration, high wiring density, using multilayer board is not only necessary for wiring, but also an effective means to reduce interference.
Reasonable selection of layers can greatly reduce the size of the printing board, can make full use of the intermediate layer to set the shield, can better realize the nearby grounding, can effectively reduce the parasitic inductance, can effectively shorten the transmission length of the signal, can greatly reduce the cross interference between signals, etc.
b) The less bent the lead, the better
The less lead bending between pins of high-speed circuit devices, the better.
The wiring lead of high-speed signal routing circuit adopts full straight line and needs to turn, which can be used as 45° polyline or arc turning. This requirement is only used to improve the holding strength of steel foil in low-frequency circuit.
In high-speed circuits, meeting this requirement can reduce the transmission and coupling of high-speed signals, and reduce the radiation and reflection of signals.
c) The shorter the lead, the better
The shorter the lead between the pins of the high-speed signal routing circuit device, the better.
The longer the lead, the larger the distributed inductance and capacitance value, which will have a lot of influence on the system’s high-frequency signal passing, but also change the characteristic impedance of the circuit, resulting in reflection and oscillation of the system.
d) The less alternations between lead layers, the better
The less interlayer alternations between pins of high-speed circuit devices, the better.
The so-called “the less interlayer alternations of leads, the better” means that the fewer holes used in the connection of components, the better. It has been measured that one hole can bring about 0.5pf of distributed capacitance, resulting in a significant increase in circuit delay, reducing the number of holes can significantly improve the speed
e) Note parallel cross interference
High-speed signal wiring should pay attention to the “cross interference” introduced by the signal line short distance parallel wiring. If parallel distribution cannot be avoided, a large area of “ground” can be arranged on the opposite side of the parallel signal line to greatly reduce the interference.
f) Avoid branches and stumps
High-speed signal wiring should avoid branching or forming Stub.
Stumps have a great effect on impedance and can cause signal reflection and overshoot, so we should usually avoid stumps and branches in the design.
The Daisy chain wiring will reduce the impact on the signal.
g) Signal lines go to the inside floor as far as possible
High frequency signal line walking on the surface is easy to produce large electromagnetic radiation, and also easy to be interfered by external electromagnetic radiation or factors.
The high frequency signal line is routed between the power supply and the ground wire, through the absorption of electromagnetic wave by the power supply and the bottom layer, the radiation generated will be much reduced.